Fastening Points

Exploring Innovations at JEC World 2024 Show: Composite Materials in Engineering
This year’s JEC World Show not only matched its predecessors in terms of interest and inspiration but also highlighted a significant shift towards the diversification and sustainable utilisation of composite materials in engineering. Our team at bigHead, present on the Bossard Group stand, had the privilege of witnessing these advancements first-hand, and we’re excited to share a comprehensive overview of the key takeaways from the event.
The Rise of Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) in Engineering
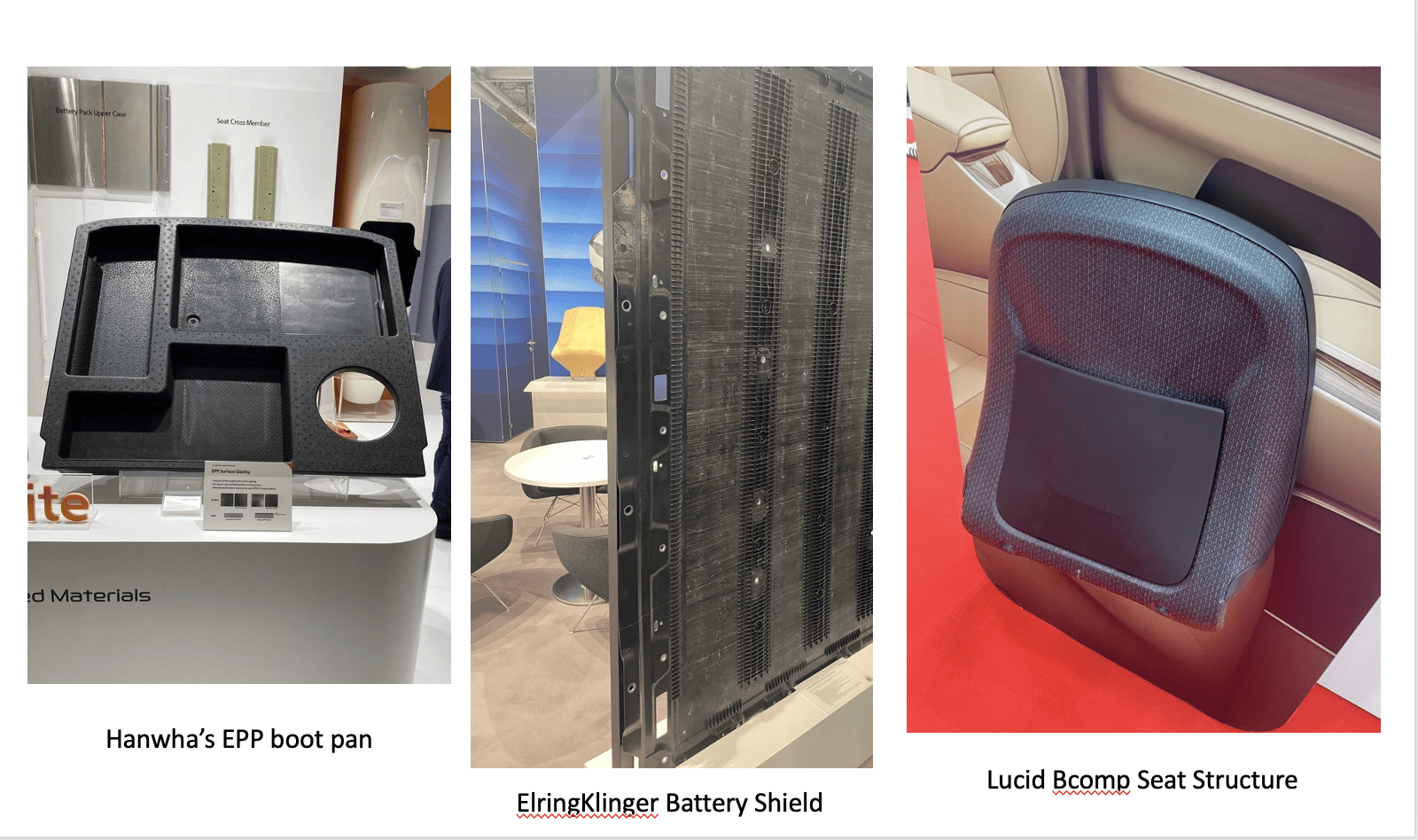
Expanded Polypropylene (EPP) has moved beyond its traditional role in packaging and is increasingly being used as an engineering material. Hanwha Advanced Materials introduced an EPP automotive boot pan, marking a significant leap in how this material is viewed within the automotive sector. EPP’s attributes, including as superior noise and vibrational insulation, along with chemical resistance, making it an ideal candidate for engineering applications. Moreover, the sustainability quotient of EPP is noteworthy being 100% recyclable. Hanwha’s “BuffLite” variant comprises at least 30% recycled content, reinforcing the industry’s commitment to recycling and sustainable material use.
Thermoplastic Composites: A Sustainable Alternative
The emphasis on thermoplastic composites was another highlight, driven by the urgent need for sustainability and end-of-life material considerations. The applications showcased were as varied as they were impressive, ranging from vehicle front-end modules and interior structures to battery pack shielding for electric vehicles (EVs). Arkema’s presentation of their Elium thermoplastic resin was particularly enlightening. Elium stands out as it can be processed using conventional thermoset resin production methods but offers the added advantage of depolymerisation at the end of a component’s life. This process allows for the reclamation and reuse of polymer monomers, showcasing a significant stride towards circular economy principles in material science.
Ongoing Focus on SMC/BMC for Automotive Applications
Sheet Moulding Compound (SMC) and Bulk Moulding Compound (BMC) continue to be focal points, especially concerning automotive body panels and EV battery packs. Discussions at JEC World 2024 honed in on strategies for reducing energy costs and enhancing manufacturing throughput for SMC/BMC processing. On that note, so called “snap-cure” resin systems can be processed with much shorter cycle times, whilst running presses at a constant temperature reduces energy consumption compared to cooling & reheating moulds/ tooling after each pressing cycle.
Natural Fibre Composites: Paving the Way for Eco-friendly Innovation
The event also showcased the burgeoning interest in natural fibre composites, particularly in the realm of vehicle interiors. A notable example was the Lucid seatback structure, crafted using BComp flax, which boasted a 50% reduction in plastic content and a 40% weight reduction compared to conventional designs. This innovation not only underscores the potential of natural fibres in reducing environmental impact but also highlights the industry’s commitment to exploring renewable resources and materials.
JEC World 2024 has highlighted new benchmarks in the pursuit of sustainability and innovation in materials science and engineering. It is clear that the focus on recyclable and environmentally friendly materials will continue to shape the trajectory of the industry, promising a greener and more sustainable future.